Bunsen burner is a gas burner that produces smokeless, nonluminous flame used for heating, sterilizing, and combustion purposes in laboratory experiments. It was named after Robert Bunsen, a German scientist who designed it in 1857. A.D.
Bunsen burner ignites by the fusion of fuel and air (oxygen). There are two primary fuel sources for bunsen burner: natural gas (methane) and liquified petroleum gas (propane, butane, or a mixture of both).
Table of Contents
- Parts of a Bunsen Burner
- Principle
- Types of Flame on a Bunsen Burner
- Safety flame
- Medium blue flame
- Roaring flame
- Types of Bunsen Burner
- Tirrill burner
- Teclu burner
- Maker burner
- Application/Uses of Bunsen Burner
- In the chemical laboratories
- Within microbiology laboratories
- In zoology and botany laboratories
- Advantages of Bunsen Burner
- Limitations of Bunsen Burner
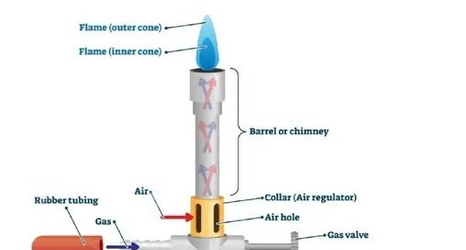
Parts of a Bunsen Burner
The Bunsen burner is an essential part of laboratory equipment used for heating materials in the laboratory.